Table of Contents
ToggleAbstract
This articles applies the PESTLE framework on Tesco to identify the key macro-environmental forces that shape Tesco’s business strategy. The strategic management teachers, students and researchers may find Tesco PESTLE analysis useful to understand how changing business environment is transforming the retail industry. Management of retail organizations may also review the results to understand the strategic implications of changing business environment.
1. Introduction
In 2022-2023, Tesco was listed as the top ranked retailer based on UK consumer rankings. As per World Economic Forum, Tesco is world’s 3rd largest retailer based on gross revenue, and 9th largest retailer based on net revenue.
Recently, the company is struggling with various issues in post-pandemic world. This article presents the PESTLE analysis of Tesco to understand how changing external environment is influencing Tesco business strategies, and how company is responding to those challenges to remain competitive in the market.
2. Company overview
| Company name | Tesco Plc |
| Type | Public limited company |
| Industry | Retail |
| Headquarters | Welwyn Garden City, UK |
| CEO | Ken Murphy |
| Number of employees | 354,744 |
| Number of stores | 4,752 |
| Revenue 2022 | $84.139 billion |
| Brand value 2022 | $9.91 billion |
3. Tesco PESTLE Analysis
Here is the PEST analysis Tesco. The environmental forces exerting positive impact are classified as ‘Opportunities’ (O) and forces exerted negative impact are classified as ‘threats’ (T).
3.1. Political factors Tesco
3.1.1. Political stability score (O)
As per most recent index, UK (Tesco’s home market) attains 0.54 average score for political stability. The political stability index has a range of -2.5 to +2.5, and world average political stability score is -0.07 points.
Following graph shows the political environment of UK has been stable since 2019:
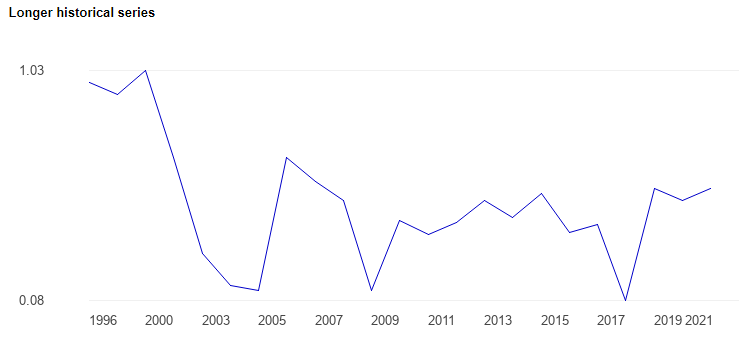
Source: Global Economy
High political stability makes business environment less uncertain for Tesco and other retailers.
3.1.2. Brexit disruption (T)
In 2022, the post-Brexit changes added to the soaring costs in UK. Recently, Guardian reported that Brexit changes will continue raising the business costs, causing customs delays, and hampering the food supply chains.
In case of Tesco, Brexit disruption has directly affected the Tesco’s cost structure. Tesco sources more than 26% food from EU, as depicted in following graph:
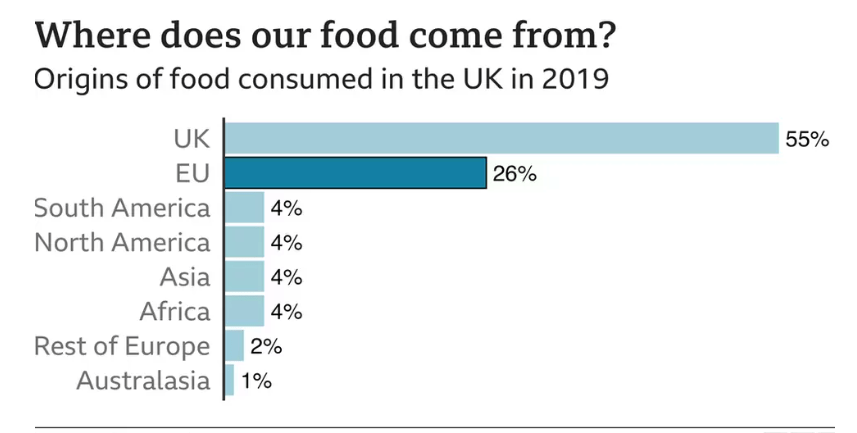
Source: BBC
So, even a slight increase in the tariffs due to harsh UK-EU relations will have serious cost implications for Tesco.
3.1.3. Global political environment (T)
Growing global political uncertainty is a serious cause of concern for Tesco, as it operates in various countries around the world. Morrisons- a close competitor of Tesco blamed political uncertainty for stalled business growth.
3.1.4. Political lobbying (O)
Tesco invests on political lobbying to influence the government decisions. Recently, Tesco joined forces with Sainsbury and Greggs to lobby UK Prime Minister for meaningful cut to business rates.
3.1.5. Changing government policies (T)
As reported by Reuters, Tesco chairman hit the UK government over frequent policy changes. For instance, UK government’s stance over anti-child obesity campaign keeps changing. The uncertainty in regulatory environment makes it difficult for Tesco and other retailers to fulfil their long-term commitments with suppliers.
3.1.6. Pandemic relief schemes (T)
During pandemic, UK government offered tax reliefs to the retailers. In post-pandemic world, Tesco is under pressure to pay back £585 million that it made from relief schemes.
3.2. Economic factors Tesco
3.2.1. Economic uncertainty (T)
The global economic uncertainty is affecting the financial performance of Tesco and other retail giants. Although, Tesco’s pre-tax profits jumped from £1.1bn to £2.2bn, the looming economic uncertainty is inducting the retail giant to keep a strict check on prices- says Guardian.
3.2.2. Rising inflation (T)
As per Bloomberg, Tesco stock has declined by 7% due to rising inflation. Following graph shows the inflation has grown to 10.1% in 2023:
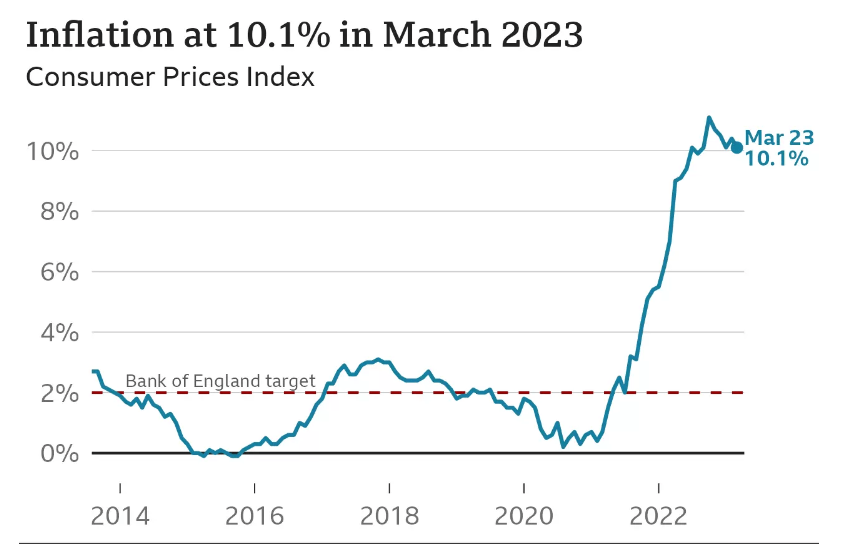
Source: BBC News
Rising inflation has squeezed the Tesco profits.
3.2.3. Post-pandemic economic recovery (O)
UK economy has quickly recovered from the pandemic impact, and fast economic rebound is paying Tesco well. In 2021, Tesco revenue rose by 5.9%, and operating profit increased by 28% compared to last year- BBC reports.
3.2.4. Growing cost cutting pressure (T)
Despite increase in profits, the retail giants like Tesco are still under pressure to cut the costs due to lack of skilled workers, wage inflation, supply chain disruptions and energy crisis. As a cost cutting measure, Tesco plans to cut thousands of jobs in 2023 amid economic uncertainty.
3.2.5 Shrinking consumer spending in UK (T)
In 2023, British Retail Consortium reported that rising inflation is inducing UK consumers to spend less, and rein on discretionary purchases. The squeezing household budget can affect the financial performance of Tesco and overall UK retail industry.
3.3. Social factors Tesco
3.3.1. Online shopping trends (O)
Despite some slowdown in online sales, the UK ecommerce sales still accounted for 35.9% of total retail sales in 2022. The growing online shopping trends present exciting growth opportunities to retailers in UK.
Following graph shows an overall rise in Tesco online sales from 2014 to 2022:
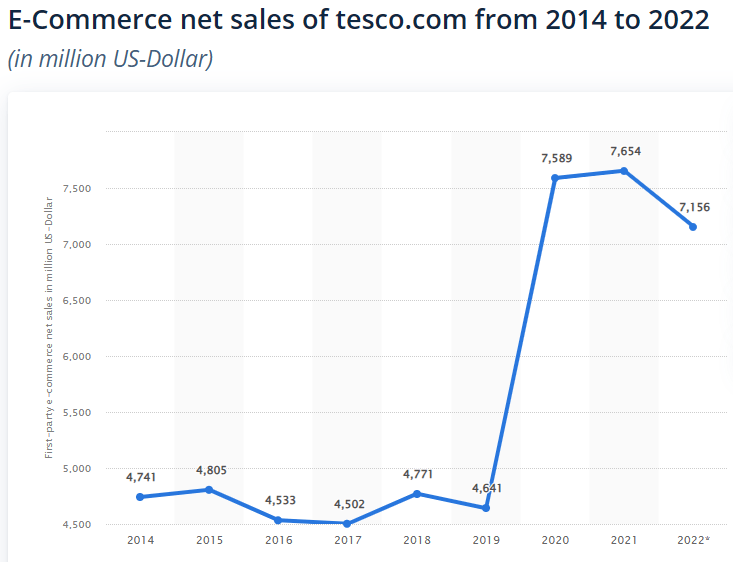
Source: Statista
3.3.2. Environmental consciousness (O)
Retail consumers in UK have started placing high importance to sustainability. A recent survey on 2,000 UK retail customers revealed that two-third of UK customers engage in sustainable consumption behavior. Tesco understands the importance of integrating sustainability, and thus, invests heavily on sustainable business practices to improve performance on all key sustainability measures.
3.3.3. Growing vegan market (O)
UK retail customers’ preferences for plant-based meat and vegan products are rising. Particularly, the young customers in UK are showing interest in following a vegan/vegetarian diet. Responding to this trend, Tesco has expanded the plant based product range by 34 new items in 2022.
3.3.4. Local norms and traditions (T)
The importance of tailoring business and marketing practices according to local cultural norms and traditions is growing. Tesco’s inability to understand the local cultural context led towards failure in Japanese retail market.
3.3.5. Changing demographics (T and O)
UK population demographics are changing. Gen Z is entering in the consumer market. Forecasts further suggest that in next 25 years, the elderly adults (above 85 years old) will grow to double. The retailers in UK must proactively respond to the changing trends to remain relevant in the market.
3.4. Technological factors Tesco
3.4.1. Adoption of Robotics technology (O)
As per Reuters, retailers in UK are investing on robotics technology to fight the cost inflation. Tesco has teamed with the Ocado partner to launch the automated warehouse robots in logistics centers across UK.
3.4.2. Virtual and augmented reality trends (O)
As per forecasts, the augmented reality will reach $61.3 billion by 2031 in retail industry. Tesco is successfully capturing this trend, and has won many awards for using augmented reality. In 2022, Tesco invested on virtual reality to test the new environmental labelling.
3.4.3. Mobile based advertising (O and T)
The mobile advertising is increasingly getting popular in retail industry. Responding to this trend, Tesco is investing on mobile advertising, but remains unable to get the desired objectives. Recently, Tesco faced criticism for offensive mobile advertising that created an outrage among customers.
3.4.4. Drone delivery (O)
UK consumers’ are becoming receptive to drone deliveries. This trend can revolutionize the global retail industry. Tesco is preparing itself for this trend by expanding the two-minute drone delivery trial in UK.
3.4.5. Green technologies (O)
As per statistics, the green technology market is expected to grow with 21.9% CAGR by 2030. Tesco is actively investing on green technologies– from solar farms to electric delivery fleets to improve its sustainability performance.
3.4.6. Cashier less billings (O)
The cashier less billing trend is on rise in UK retail industry. Tesco has partnered with Amazon Go to revolutionize the shopping process through error-free billing.
The above discussion covers the PEST analysis of Tesco. Tesco pest analysis only covers political, economic, social and technological factors.
After conducting PEST analysis for Tesco, now the analysis is stretched to two additional forces- legal, and environmental.
3.5. Legal factors Tesco
3.5.1. Trademark and copyright laws (T)
The patent infringement and copyright laws are getting strict with time. In 2023, Tesco lost a trademark lawsuit against Lidl, which not only incurred economic costs, but also damaged the brand reputation.
3.5.2. Customer protection laws (T)
The growing internet use increases the risk cyberattacks. In 2018, Tesco paid £16.4 million in fine for failings to protect its customers’ online information.
3.5.3. Employee protection laws (T)
The UK legislation system protects the employees from abusive work practices. In 2022, Tesco faced lawsuits for keeping its migrant workers in stressful and inhumane work conditions. Such lawsuits hurt Tesco’s image as a responsible corporate citizen.
3.6. Environmental factors Tesco
3.6.1. Rising emission standards (T and O)
The emission standards for retail businesses are getting strict in UK. However, Tesco is taking this pressure as an opportunity, and aims for ‘net zero’ emissions across whole supply chain by 2050.
3.6.2. Circular economy regulations (T and O)
The waste amendment regulations in UK compel business organizations to increase recycling, and adopt a more responsible attitude towards environment. Tesco is responding to this pressure by investing on the soft plastic recycling.
3.6.3. Ban on single use plastic (T and O)
In UK, ban over single use plastic is creating packaging challenges for retailers. However, by adopting a proactive response, Tesco is actively eliminating the unnecessary packaging to build sustainable and green brand image.
The overall PESTLE analysis for Tesco is summarized below:
4. Summary- PESTLE Analysis on Tesco
| PESTEL Analysis of Tesco | ||
| Political factors Tesco • High political stability • Brexit disruptions • Global political uncertainty • Political lobbying • Changing government policies • Pandemic relief schemes | Economic factors Tesco • Economic uncertainty • Rising inflation • Post-pandemic recovery • Growing cost cutting pressure • Shrinking consumer spending | Social factors Tesco • Online shopping trends • Growing environment consciousness • Growing vegan market • Local norms and traditions • Changing consumer demographics |
| Technological factors Tesco • Adoption of Robotics technology • Virtual and augmented reality trends • Mobile based advertising • Drone delivery • Green technologies • Cashier less billings | Legal factors Tesco • Trademark and copyright laws • Customer protection laws • Employee protection laws | Environmental factors Tesco • Rising emission standards • Circular economy regulations • Ban on single use plastic |
Pestle analysis Tesco
5. Recommendations based on Tesco PESTEL Analysis
Based on Tesco PESTEL analysis, we propose following recommendations:
• Invest more on the automated robotics technology to reduce costs.
• Expand drone delivery as UK retail customers are becoming more receptive to it.
• Launch more products/services for elderly adults as their proportion is growing.
• Ensure effective implementation of customer protection, employee rights and copyright law to avoid lawsuits.
• Take more rigorous sustainability measures to build positive brand image
• Tailor business strategies according to local norms and traditions
• Launch more vegan/vegetarian products for growing vegetarian/vegan market
6. Conclusion
Tesco PESTEL analysis highlights various environmental factors that have strategic implications for the organization. To achieve long-term success, Tesco must proactively respond to changing external environment by leveraging its key strengths, and overcoming its weaknesses.
This article took an outward view to evaluate the Tesco business strategies. Have a look on our article ‘Tesco SWOT analysis’ to take an inward view of company.
Another recommended read is Tesco Corporate Social Responsibility.
7. References
Houlton, C. (2023, February 7). Tesco, Sainsbury’s and Waitrose among top ranked retailers. Grocery Gazette – Latest Grocery Industry News.
Tesco. (n.d.). World Economic Forum.
United Kingdom Political stability – data, chart | TheGlobalEconomy.com. (n.d.). TheGlobalEconomy.com.
United Kingdom Political stability – data, chart | TheGlobalEconomy.com. (n.d.-b). TheGlobalEconomy.com.
Partington, R., & Jolly, J. (2022, January 10). Brexit changes will add to soaring costs in 2022, warn UK manufacturers. The Guardian.
BBC News. (2020, December 27). Tesco: Brexit impact on food prices “very modest.” BBC News.
Admin, & Admin. (2023ab, April 12). Costa Coffee PESTLE Analysis – Complete PESTEL Analysis. Strategy Finders.
Admin, & Admin. (2023ac, April 12). Costa Coffee PESTLE Analysis – Complete PESTEL Analysis. Strategy Finders.
Hawkins, E. (2022, May 3). Tesco, Sainsbury’s and Greggs join forces to lobby Sunak to slash business rates. CityAM.
Davey, J. (2022, June 17). Tesco chairman hits out at UK government over policy changes. Reuters.
Jahshan, E. (2020, December 2). Tesco to pay government £585m it saved from business rates holiday. Retail Gazette.
Sweney, M. (2022, April 13). Tesco focused on keeping prices ‘in check’ as profits double. The Guardian.
Linsell, K. (2022, April 13). Tesco Faces Profit Squeeze as Inflation Threatens Spending. Bloomberg.com.
BBC News. (2023, May 11). What is the UK inflation rate and why is the cost of living rising? BBC News.
BBC News. (2021, October 6). Tesco shrugs off supply concerns as sales surge. BBC News.
UK consumer spending drops as inflation bites | GC Business Growth Hub. (n.d.). GC Business Growth Hub.
Team, O. C. (2023). The 10 Best Ecommerce Trends in the UK To Grow Your Business. Osome UK.
Statista. (2023e, May 11). tesco.com: E-Commerce net sales from 2014 to 2022.
UK shoppers: sustainable shopping behaviors 2022 | Statista. (2022, August 9). Statista.
Admin, & Admin. (2023y, March 7). Beyond Meat SWOT Analysis 2023. Strategy Finders.
Tesco’s Plant-Based Range Expands With 34 New Products. (2022, September 14). Vegconomist – the Vegan Business Magazine.
Our ageing population. (n.d.). The Health Foundation.
Davey, J. (2022b, December 1). Analysis: Retailers turn to robots in cost inflation fight. Reuters.
Admin, & Admin. (2023r, January 13). Walmart SWOT Analysis 2022 | In-depth SWOT Study of Walmart. Strategy Finders.
Admin, & Admin. (2023s, January 13). Walmart SWOT Analysis 2022 | In-depth SWOT Study of Walmart. Strategy Finders.
Augmented Reality in Retail Market Statistics | Forecast – 2031. (n.d.). Allied Market Research.
Lee, B. J. (2022, May 11). Tesco Mobile advertising campaign offensive, watchdog rules. BBC News.
Admin, & Admin. (2023f, January 11). Comprehensive Analysis Of Walmart Marketing Strategy. Strategy Finders.
Green Technology and Sustainability Market | Forecast – 2030. (n.d.). Allied Market Research.
Admin, & Admin. (2023n, January 12). SWOT Analysis of Apple | Strengths and Weaknesses revealed. Strategy Finders.
Admin, & Admin. (2023ai, May 2). T Mobile SWOT Analysis – SWOT Analysis by Marketing Experts. Strategy Finders.




