Table of Contents
ToggleAbstract
This article presents a critical analysis of Tata Motors’ key business strategies. The detailed analysis provides insights into how Tata Motors is responding to the internal and external environmental challenges, and how it could perform better to strengthen the competitive positioning in the market. The article is particularly useful for the strategic marketing/management students, researchers and teachers. Market researchers and practitioners may also read the article to understand the current dynamics of Indian automobile industry.
1. Introduction
In 2023, Tata Motors dethroned the Maruti Suzuki, and became India’s most favorite automotive brand. This Tata Motors Case Study explores the key reasons behind company’s success by applying SWOT framework.
The SWOT analysis of Tata Motors highlights the key factors that support or threaten the company’s competitive positioning in the market.
2. Company overview
| Company name | Tata Motors |
| Type | Public Limited Company |
| Year founded | 1945 |
| Headquarters | Mumbai |
| CEO | Guenter Karl Butschek |
| Number of employees | 78,906 |
| Number of countries | 26 countries across four continents |
| Number of outlets | 951 authorized showrooms |
| Tata Motors revenue 2022 | 2,957.71 crore (295% growth from 2021) |
| Tata Motors brand value 2023 | $23.19 billion |
Key products of Tata Motors: Cars and sports utility vehicles, trucks, buses and defense equipment
Key Competitors of Tata Motors: Mahindra, Maruti Suzuki, Toyota, Skoda
3. SWOT Analysis of Tata Motors
Here, we present the SWOT analysis of Tata group by identifying Tata Group’s key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats.
3.1. Tata Motors Strengths
3.1.1. High market share
As per Economic Times, Tata Motors has the market share of 13.57% in 2022. The latest data suggests that in 2023, Tata Motors is India’s third largest automotive brand, based on market share:
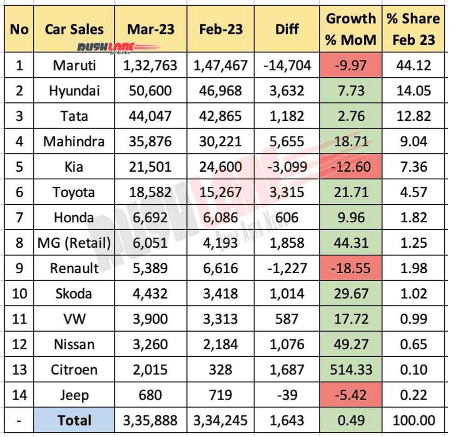
Source: Rushlane.com
3.1.2. Wide distribution network
Tata Motors has wide distribution network that is spread across the globe. Tata Motors’ dealer network covers 8,800 touch points in 125 countries. In home country, Tata covers 90% of India with 250 dealers spread across 195 cities, and 27 states.
3.1.3. Second highest car manufacturer
Tata Motors became India’s second largest car manufacturer with an impressive 185% year-on-year growth.
3.1.4. Low-cost strategy
With an experience of over five decades, Tata Motors has successfully implemented low cost strategy. The company offers an unmatched value for money by serving the customers’ varied needs through a diverse range of products.
3.1.5. Well-diverse product portfolio
Tata Motors has a well-diverse product portfolio. Its 2022 annual report revealed that Tata Motors was able to grow revenue from commercial and electric vehicles. Its commercial vehicles volume grew by 37%, and revenue grew by 58%. Its electric vehicles volume grew by 67%, revenue grew by 90%.
3.1.6. Strong presence in electric vehicle market
Tata Motors continues to dominate the electric vehicle segment. In 2023, Tata Motor has 86% market share in Indian electric vehicle market from Tigor EV and Nexon EV.
3.1.7. Consistent revenue growth
Tata Motors has reported a consistent revenue growth from 2010 to 2022, as depicted in following graph:

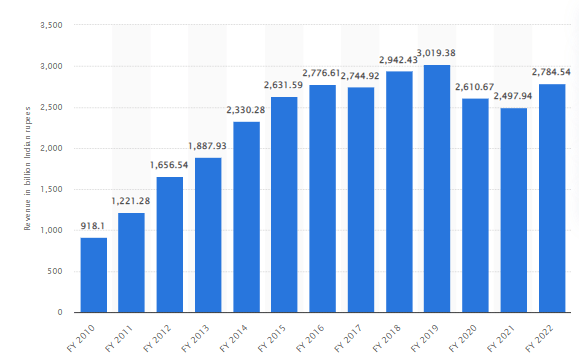
Source: Statista
3.1.8. Successful strategic acquisitions
Tata Motors has a series of successful strategic acquisitions. The most recent example is successful acquisition of JLR that helped company in acquiring the global footprint.
3.1.9. High customer satisfaction
Tata Motors leads the automobile industry not only in terms of sales, but also in terms of customer satisfaction. With a score of 29.6, Tata Motors became Indian automobile customers’ most favorite brand in 2023.
3.1.10. High global recognition
Tata Motors ranked 31 out of 2000 on Forbes’ ‘best companies’ list. Company was also recognized among top 5 ranked global auto manufacturers in 2019.
3.2. Tata Motors Weaknesses
3.2.1. Perceived poor quality
As per Business Standard, Tata Motors struggles with the poor quality and service responsiveness issues, which exerts an adverse impact on the brand.
3.2.2. Nexon EV controversy
Tata Motors’ Nexon EV range is currently under threat of getting delisted from the vehicles eligible for government benefits under EV policy.
3.2.3. Weak international presence
Tata Motors has comparatively weak presence at international stage than its key competitors like Toyota and Honda:
| Automotive companies | Number of countries |
| Toyota | 170 countries |
| Honda | 140 countries |
| Maruti Suzuki | 100 countries |
| Mahindra Group | 100 countries |
| Tata Motors | 26 countries |
3.2.4. Poor performance in luxury segment
Tata Motors is unable to perform well in the luxury segment. In 2022, Tata Motors’ JLR revenue fell by 7%. Due to weak performance in luxury segment, JLR driven Tata Motors into a loss of Rupees 5000 crore in 2022.
3.2.5. Slow pandemic recovery
The pandemic negatively affected the Tata Motors’ sales volume. Although, company is recovering from pandemic effects, the post-pandemic sales volume has not reached the pre-pandemic growth level:

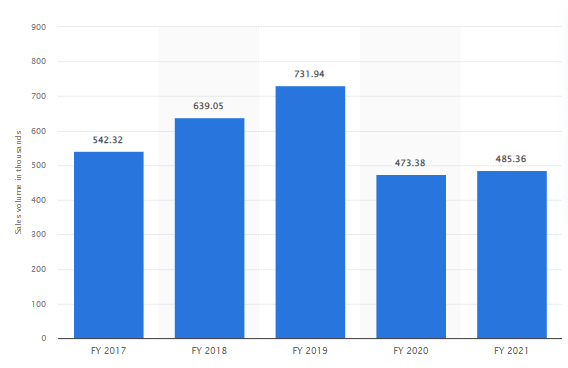
Source: Statista
3.2.6. Declining profit growth rate
Although, Tata Motors recorded a profit of Rs 5,408 crore in 4th quarter of 2022, but its overall profitability rate has declined with time. Following graph shows the overall profitability trend from 2016 to 2021:

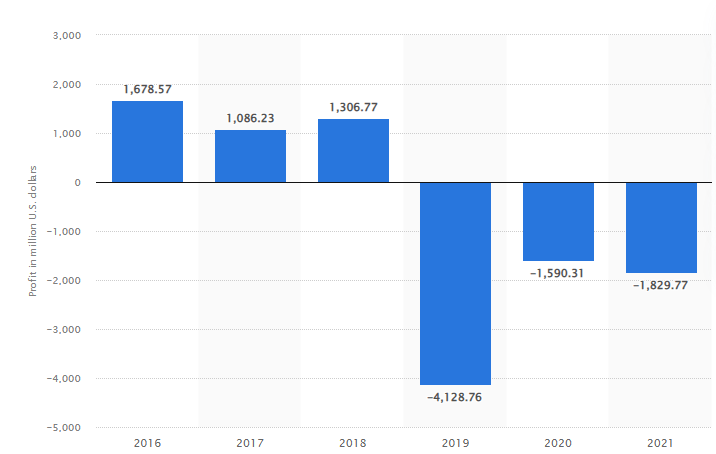
Source: Statista
3.2.7. Flawed marketing strategies
Tata Motors’ marketing strategies are hyper-local, which limit the company’s exposure to international market. Tata Nano presents another example of poor marketing strategy. Tata Motors advertised its Nano model as a cheap car, which negatively affected the people’s perceptions about product quality, and led the product towards failure.
3.3. Tata Motors Opportunities
3.3.1. Expansion of luxury vehicle industry
Indian luxury car market is expected to grow from$1.2 billion in 2020 to $1.7 billion in 2030:

Source: Verified market research
Although, Tata Motors is not functioning well in luxury segment, but considering the growth trend, the company can turn its weakness into an opportunity to expand presence in luxury car market.
3.3.2. Growth in electric vehicle market
Indian electric vehicle market will grow with 44.5% CAGR from 2020 to 2025. It presents a growth opportunity to the Tata Motor’s EV segment.
3.3.3. Sustainable mobility
The automobile customers’ demand for the sustainability mobility is rising. Tata Motors has launched ‘go green initiative’ in 2020 to grab the attention of environment conscious customers. The company should invest more on green marketing efforts to capture this trend.
3.3.4. International expansion
As per Global News Wire, global automotive industry will grow with 6.9% CAGR by 2030.
Following graph shows that in 2023, the most attractive regions with high growth potential are Asia, North America, and Western Europe:
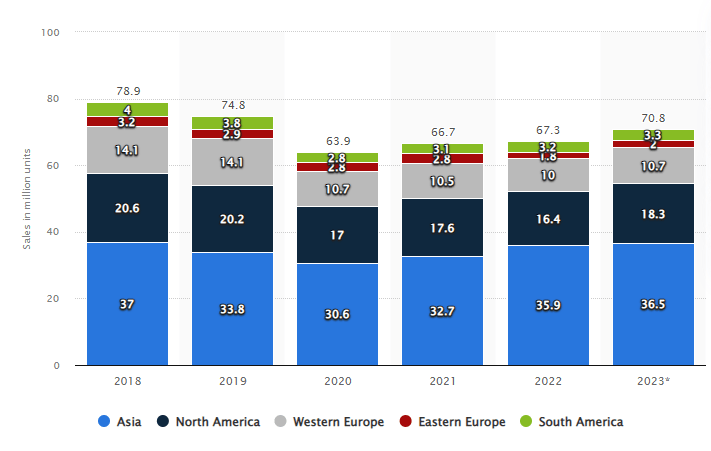
Source: Statista
As Tata Motors has limited presence at international stage, it can turn the weakness into strength by expanding its operations to the Asia, North America and Europe.
3.3.5. Hydrogen fuel cell market size
The global hydrogen fuel sell market is expected to grow with an impressive 59.4% CAGR, from $0.65 billion in 2021 to $43.19 billion by 2030:
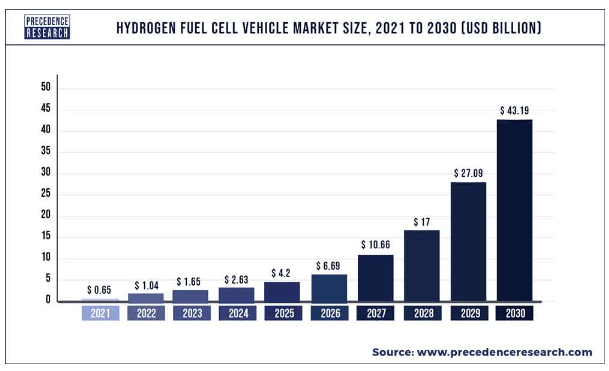
Source: Precedence Research
The company has already started investing on hydrogen fuel cell technology, and has filed for six international patents. The impressive growth rate suggest Tata Motors to invest more on this technology.
3.3.6. CNG powered vehicle market
Indian CNG powered vehicle sales has increased by 41% in 2022 compared to 2021, accounting for 8.8% of total passenger vehicle sales in India. Tata Motors has already recognized this trend. In 2022, 16% of its commercial vehicle sales came from CNG-powered vehicles, showing a rise of 12.6% from 2021.
3.4. Tata Motors Threats
3.4.1. Anti-trust lawsuits
A story of Reuters revealed that Tata Motors is currently facing anti-trust lawsuits by two finance firms. These lawsuits have put Tata Motors under the radar of Indian regulatory authorities.
3.4.2. Semi-conductor chip shortage
As per Hindustan Times, semi-conductor chip shortage issue is likely to worsen in coming years. It may cause supply chain disruptions, and affect the automobile production in India.
3.4.3. Intense competition at local and international stage
The competition in local and international automotive industry is getting intense with time. The market is getting saturated, limiting the growth opportunities for existing players.
3.4.4. Inflationary pressure
The inflationary pressure and rising production costs are negatively affecting the revenue and profit margins of Indian automobile manufacturers.
3.4.5. Rising fuel prices
As per Times of India, the consistent rise in the fuel prices may lower the fuel demand by 1.5% by 2030. Rising fuel prices may compel automobile manufacturers to shift to CNG powered, and electric vehicle segments.
3.4.6. Cybersecurity issues
The connected vehicles are revolutionizing the auto industry, but they are also vulnerable to the cyberattacks. In 2022, Tata Motors’ IT system was affected by a cyberattack. Tata Motors must take serious measures to mitigate this threat to avoid financial and reputational damage.
3.4.7. Growing regulatory burden
As per Economic Times, the top automakers in India are blaming the regulatory burden and high taxes responsible for slowing down the automotive industry growth from 12% (2021) to 3% (2022).
4. Summary – SWOT of Tata Motors
| Tata Motors Strengths High market share Wide distribution network Second highest car manufacturer Low cost strategy Well-diverse product portfolio Strong presence in EV market Consistent revenue growth Successful strategic acquisitions High customer satisfaction High global recognition | Tata Motors Weaknesses Perceived poor quality Nexon EV controversy Weak international presence Poor performance in luxury segment Slow pandemic recovery Declining profit growth rate Flawed marketing strategies |
| Tata Motors Opportunities Expansion of luxury vehicle segment Growth in the electric vehicle Sustainable mobility International expansion Hydrogen fuel cell technology CNG powered vehicle market | Tata Motors Threats Anti-trust lawsuits Semi-conductor chip shortage Intense competition Inflationary pressure Rising fuel prices Cybersecurity issues Growing regulatory burden |
TATA Motors SWOT Analysis
Based on SWOT analysis of Tata Company, we propose following recommendations:
5. Recommendations
• Resolve the quality related concerns by taking strict quality control measures
• Expand business operations in the emerging economies to strengthen international presence
• Adopt marketing strategies that could support the international expansion
• Invest more on the EV, CNG powered and hydrogen fuel cell market.
• Invest on green marketing efforts to position Tata Motors as a sustainable automotive brand
• Take cost reduction measures to avoid price hikes and increase profitability
• Conduct market research to better understand the luxury automotive consumers’ preferences and expectations
6. Conclusion
This Tata motors case study suggests that Tata Motors currently holds a strong position in the market. However, the prevailing economic uncertainty, regulatory pressure and Tata Motors’ weak international presence are some key factors that company should pay immediate attention. The analysis also highlights various opportunities that Tata Motors can consider to strengthen its competitive position in the automobile market.
7. References
Pti. (2023, March 7). Maruti, Hyundai market share dips in February; Tata Motors, Mahindra register gain: FADA. The Economic Times.
Market of Tata Motors – Top Car Manufacturers in the World. (2022, January 19). Tata Motors Limited | Largest Indian Automobile Manufacturer.
Garg, A. (2022, June 4). Tata Motors becomes second highest car maker in India, leaves Hyundai behind. Zee News.
The Hindu Bureau. (2023, February 16). India’s electric vehicle market grew 223% in 2022.
Statista. (2023b, May 10). Revenue of Tata Motors FY 2010-2022.
Tata Motors dethrones Maruti Suzuki to top YouGov’s Auto Rankings 2023 in India. (n.d.).
Tata Motors ranked 31 out of 2000 and 5th amongst the global automobile manufacturers in Forbes’ World’s Best Regarded Companies 2019. (2020, May 19). Tata Motors Limited.
Press Trust of India, Press Trust of India, & Business Standard. (2016, December 9). Tata Motors suffered from legacy products, quality issues: Mistry. www.business-standard.com.
Tnn. (2022, July 28). Jaguar Land Rover drives Tata Motors into a Rs 5,000 cr loss. The Times of India.
Statista. (2022b, December 22). Net sales volume of Tata Motors FY 2017-2021.
Now, E. (2023, May 12). Tata Motors Q4 Results: Net profit at Rs 5,408 crore; revenue jumps 35% YoY. The Economic Times.
Statista. (2023c, May 10). Tata Motors – net profit 2016-2021.
Khan, I. (2023, April 6). How Indian EV industry is raising the temperature of global market. Times of India Blog.
Future, M. R. (2023, May 1). Automotive Industry Projected to Reach USD 6,070.4 billion, with a CAGR of 6.9% by 2030 – Report by Market Research Future (MRFR). GlobeNewswire News Room.
Statista. (2023b, March 29). International automobile sales by region 2018-2023.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicle Market Size, Report 2022-2030. (n.d.).
Autocar Professional. (n.d.). CNG car sales scale new high in India, jump 41% in FY2023. Autocar Professional.
Syed, A. (2022, March 9). Tata Motors: Leading change with innovation – Manufacturing Today India. Manufacturing Today India.
Kalra, A. S. A. (2020, February 27). Tata Motors, two group finance firms accused of antitrust violations in India: sources. U.S.
Chakravarty, S. (2022, December 23). Goodbye 2022: Five big hurdles faced by Indian automotive industry this year. HT Auto.
Dutta, S. (2021, November 22). India’s fuel demand growth seen shrinking to 1.5% by 2030 on clean energy drive. The Times of India.
Anand, A. (2022, October 16). Tata Power’s IT Systems affected due to cyberattack; here’s all you need to know. Financial Express.
Online, E. (2022, December 20). India’s top automaker blames regulatory burden, high taxes for keeping cars out of reach. The Economic Times.




