Table of Contents
ToggleBeing world’s largest aerospace company, with the net worth of $123.24 billion (2023), Boeing makes an interesting case study for this article. What makes Boeing unique is- its ability to make close business relations even with competitors.
Boeing strategic analysis highlights various strengths and weaknesses that determine company’s strategic positioning in the market.
Before presenting in-depth Boeing SWOT analysis, let’s take a look over some basic company information:
1. Company overview
| When was Boeing established? | 1916 |
| Current CEO | Dave Calhoun |
| Number of countries | 150 countries |
| Headquarters | Arlington, Virginia, United States |
| Boeing revenue | Revenue 2022: $66.61 billion Growth compared to 2021: 6.94% |
| Boeing market capitalization (2023) | $123.24 billion |
| Boeing profit margin (2022) | $-4.94B |
Source: Macro-trends
What is Boeing known for?
For offering commercial / military aircraft| satellites| weapons| defense and electronics| information and communication systems| performance based logistics
Who are Boeing’s competitors?
Airbus| Bombardier| Embraer| COMAC| Raytheon technologies| BAE systems| Lockheed Marin| KEYW Corporation
Who is Boeing’s biggest competitor?
Airbus
2. Boeing SWOT Analysis 2022
SWOT analysis of Boeing identifies strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats:
2.1. Boeing strengths
2.1.1. Boeing business model resilience
During pandemic, Boeing cut down 787 production (most affected model as more than 35% of the components came from Japan), and increased 737 NG production. In difficult times, Boeing business model proved to be resilient as company flexibly reacted to the incident by shifting the demand to different types of aircrafts.
2.1.2. Efficient and economic aircraft models
Boeing strategic plan is set on path to success. Boing estimates that customers will seek 20% to 30% cost savings on existing models. Responding to the rising cost pressure, Boeing plans to launch more economical, mid-sized plans by 2035.
2.1.3. Wide variety
Boeing offers widest variety of air jets, ranging from commercial airlines, corporate jets and small personal jets. It has a clear edge over airbus in military jet category.
Following graph shows Boeing’s number of gross orders exceed the Airbus from 2006 to 2021:

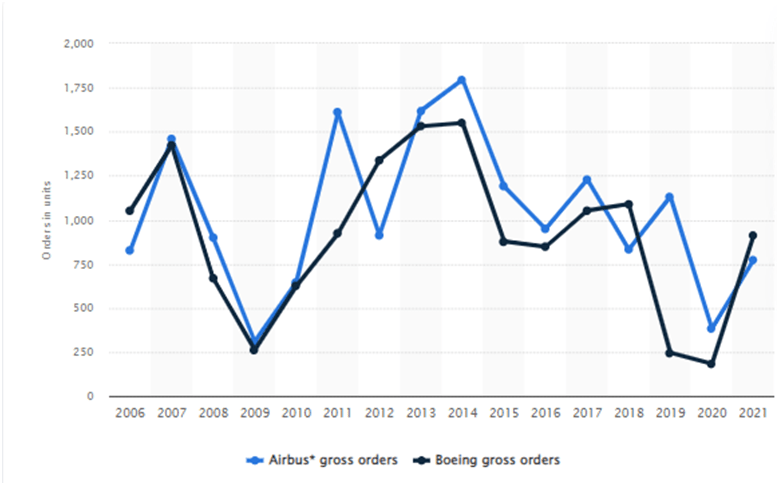
Source: Statista Research Department
2.1.4. Sustainable innovation
Boeing places central importance to the innovation, and its every business decision is geared towards developing sustainable brand future. Boeing business strategy is based on three pillars- innovate for performance, excellence in sustainability, and inspire global collaboration.
It means- innovation, sustainability and collaboration are three core areas that will determine Boeing business strategies in future.
Here is a brief snapshot of Boeing’s sustainability goals 2025:

Source: Boeing
2.1.5. Strategic partnerships
Boeing considers its strategic partners as a valuable asset, and one of the key reasons behind company’s success. Recently in 2022, Boeing developed a multi-cloud partnership with Amazon, Google and Microsoft to make key technological advancements that will enable company to transform aerospace design and manufacturing.
2.1.6. Best employer
Boeing attained 10th position in Forbes’s best employer list 2022, showing the company has developed a stronger employer brand image.
2.1.7. Less noisy airplanes
The 40% noise reduction in Boeing 737-8-200 jets have provided the company a competitive edge over rivals. Two recent examples are- Boeing 737 and 777x that have been incredibly quiet despite having huge size.
2.1.8. Go-to-Market strategy & strong geographic presence
Boeing is well-known for its go-to-market strategies, which enabled company to successfully expand its business operations to more than 150 countries. While, its closest competitor- Airbus is present in 140 countries.
2.2. Boeing Weaknesses
2.2.1. Declining revenue
Due to intensifying competition, Boeing is unable to achieve revenue growth objective. In 2007, it made annual revenue of $66,387 million, and in 2022, it made $62,286 million:

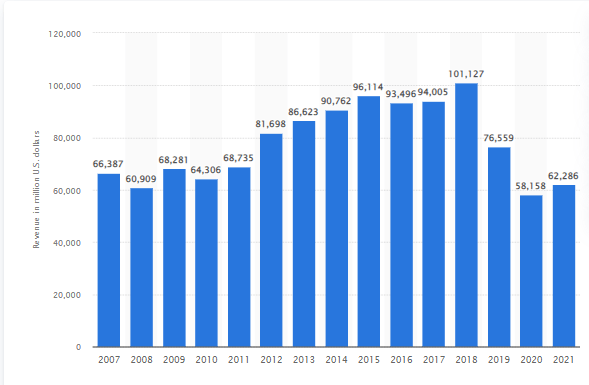
Source: Statista
2.2.2. Net loss
Boing is unable to make net profit for last five years:
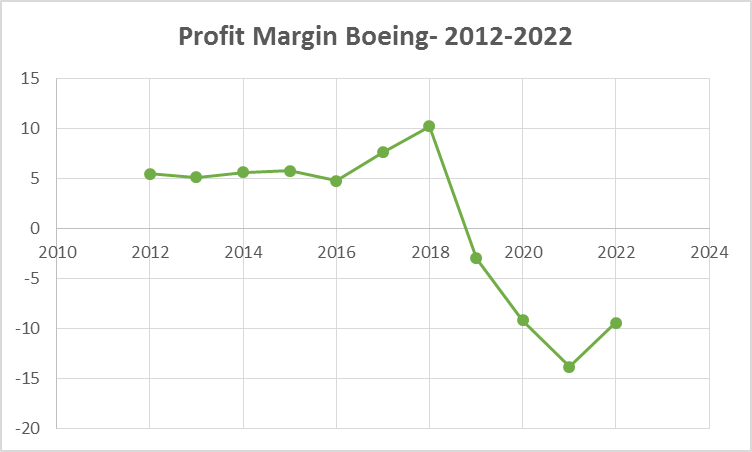
2.2.3. Losing market share
Boeing competitive analysis indicates that for last consecutive four years, Boeing orders trail Airbus. Reuters reported that in 2022, Boeing won 774 new orders, and delivered 480 airplanes. While, Airbus won 1,078 jet orders, and delivered 661 jets.
Following graph shows Boeing is at third number based on revenue, while Lockheed Martin and Raytheon technologies take first two spots:
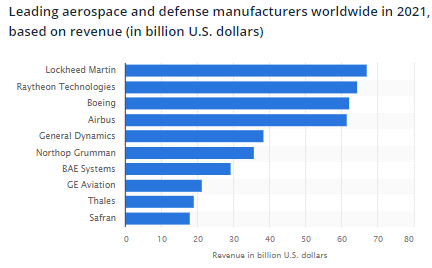
Source: Statista
2.2.4. Declining R&D expenditure
Due to thinning profit margin, Boeing is forced to cut down the R&D expenditure, resulting into making many bad product development decisions (e.g. 737 Max failure) that heavily costed the organization. Following graph shows a declining trend of Boeing’s R&D spending over time:
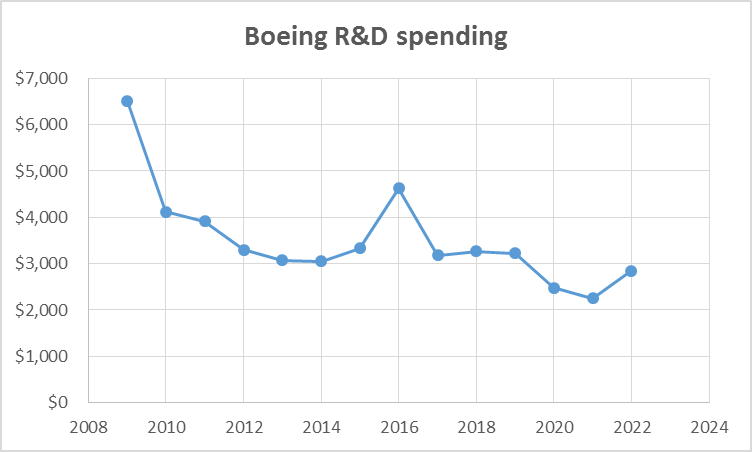
Source: Macro-trends
2.2.5. Safety issues
Boeing 737 plane crash raised serious concerns over the aircrafts’ safety. Wall Street Journal reported how Boeing failed to give complete information about cockpit safety due to which its single aisle jets are still awaiting regulatory approval.
2.2.6. Supply chain challenges
In 2022, Boeing recorded more than $5 billion loss due to supply chain disruptions and labor instability. The supply chain woes are affecting the company’s profitability, causing net loss years over years.
2.2.7. Reliance on US government
Boeing excessively relies on the U.S government, which is one of its key weakness. As per Seeking Alpha, Boeing’s 89% of defense and security revenue comes from the U.S government.
2.2.8. Extreme appetite for outsourcing
Critics argue that Boeing’s extreme appetite for outsourcing has taught brand a costly lesson. Due to poor outsourcing decision, 787 Dreamliner costed billions of dollars over budget, and got delayed by three years.
2.3. Boeing opportunities
2.3.1. Growing space market
The space market is expected to grow with CAGR of 12.25% from 2022 to 2029. Boeing has already partnered with NASA to launch its first rocket, and should further seek such collaborations to penetrate further in the space market.
2.3.2. Rising demand for satellite technology and services
Demand for satellite services is expected to grow with a CAGR rate of 6.5% from 2022 to 2028. Boeing may expand its presence in satellite market by building adaptable satellites.
2.3.3. Growing electric aircraft market
Electric aircraft market size is expected to grow from $10.93 (2021) to $39.61 (2030):
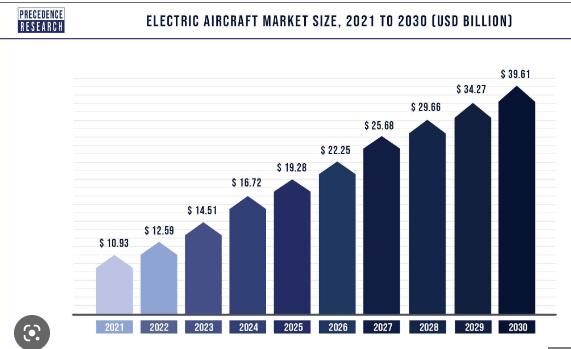
Source: Precedence Research
Boeing has collaborated with NASA and General Electric to exploit this opportunity by launching electric planes.
2.3.4. Rising demand for economical, midsized planes
There is consistent rise in demand for more mid-sized, fuel efficient planes. Boeing is planning to increase the midsized planes category in coming years.
2.3.5. Flying taxis
The flying taxi market is set to revolutionize the world. CNBC reported that Boeing is investing $45 million on developing a flying passenger vehicle, which will be launched by 2028.
2.4. Boeing Threats
2.4.1. Intensifying competition
The intensifying competition from Airbus with strong EU backing is making business environment increasingly harsh for Boeing. Following graph shows how Boeing is losing the market to Airbus:
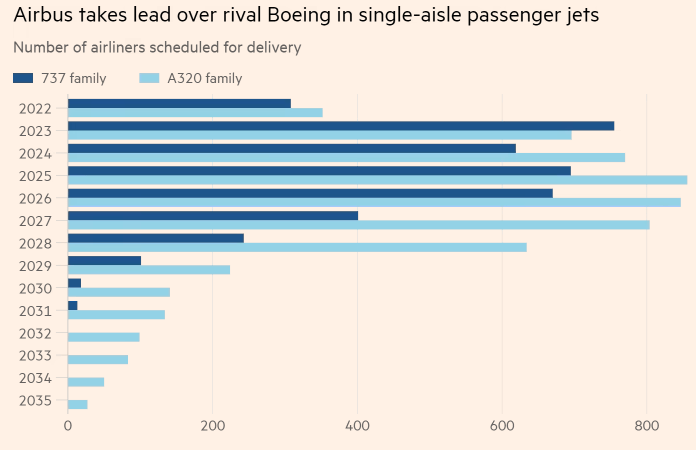
Source: Financial Times
2.4.2. Growing safety concerns
Due to consistent rise in the fatal accidents, the air travelers are increasingly concerned towards travel safety. A survey in 2020 with air travelers showed around 85% of the passengers remain concerned towards plane safety, and this figure is somehow consistent with previous years (2019- 87% and 2018- 84%).
2.4.3. Rising oil prices
Rising oil prices are hurting the aerospace industry by reducing the demand for aircrafts. Boeing understands the intensity of this risk, and is therefore, diversifying its portfolio by adding more fuel-efficient, mid-sized, and electrical vehicles.
2.4.4. Cybersecurity threat
The cybersecurity threat has risen more than ever before. Although, Boeing says that is has robust security system, but malicious hackers can target the Boeing 787 due to its security flaws.
2.4.5. Economic recession
Economic recession and reducing purchasing power can encourage the customers to prefer bus/train over air travel to save money. It can affect the airline industry, and reduced air travel demand will eventually affect the Boeing and its competitors.
3. Boeing SWOT Summary
SWOT analysis Boeing
| Boeing Strengths Resilient business model Efficient and economic models Wide variety Sustainable innovation Strategic partnerships Best employer Less noisy airplanes Go-to-market strategies | Boeing Weaknesses Declining revenue and net loss over years Losing market share Declining R&D expenditure Safety issues Supply chain challenges Reliance on US government Poor outsourcing management |
| Boeing Opportunities Growing space market Rising demand for satellites Growing electric aircraft market Rising demand for mid-sized planes Flying taxis | Boeing Threats Intensifying competition Growing safety concerns Rising oil prices Cybersecurity threat Economic recession |
4. Recommendations
• Responding to growing price sensitivity, launch more fuel efficient, mid-sized aircrafts
• Invest more on satellite technology
• Resolve customers’ safety issues and address the security flaws to reduce cyber security threat
• Reduce reliance on US government by diversifying the portfolio
• Decrease outsourcing by learning from previous mistakes
• Grow presence in the space market
• Launch more electric airplanes and flying electric taxis
5. Conclusion
Boeing strategic analysis reveals that company is currently facing various internal and external issues. However, company is in a position to handle these challenges, and perform well in future.
6. References
Boeing Net Worth 2010-2022 | BA. (n.d.). MacroTrends.
Boeing Net Profit Margin 2010-2022 | BA. (n.d.). MacroTrends.
Resilience, A., & Resilience, A. (2021, March 15). Resilience strategies for complex supply chains: Boeing – About Resilience. About Resilience -.
Hendry, J. E. (2022, November 4). Boeing Shelves Plans For Any New Midsized Airplane Until 2035. Simple Flying.
Statista. (2022a, August 26). Airbus and Boeing: aircraft orders 2006-2021.
Environmental Innovation, Conservation & Leadership. (n.d.).
Boeing named one of ‘America’s Best Employers for Veterans.’ (n.d.).
Russell, M. (2022, May 30). Stansted Airport Is Noticing How Quiet Ryanair’s Boeing 737 MAXs Are. Simple Flying.
Boeing’s worldwide revenue 2007-2021 | Statista. (2023, February 3). Statista.
Shepardson, D. (2023, January 11). Boeing orders jump but trail Airbus for 4th straight year as China lags. Reuters.
Statista. (n.d.). Statista – The Statistics Portal.
Boeing Research and Development Expenses 2010-2022 | BA. (n.d.). MacroTrends.
Tangel, A. (2022, October 17). FAA Pushes Boeing to Review Safety Documents on New 737 MAX Model. WSJ.
Kolchev, I. (2022, October 15). How Much Do Government Contracts Contribute To Defense Suppliers’ Revenue Share? Seeking Alpha.
Factors, F. &. (2022, August 4). Demand for Global Satellite Market Size & Share to Surpass USD 4,763.9 Million by 2028, Exhibit a CAGR of 6.5% | Industry Trends, Growth, Value, Analysis & Forecast Report by Facts & Factors. GlobeNewswire News Room.
Redirect Notice. (n.d.).
Georgiadis, P., & Pfeifer, S. (2022, July 18). Airbus climbs past Boeing in single-aisle market share. Financial Times.




